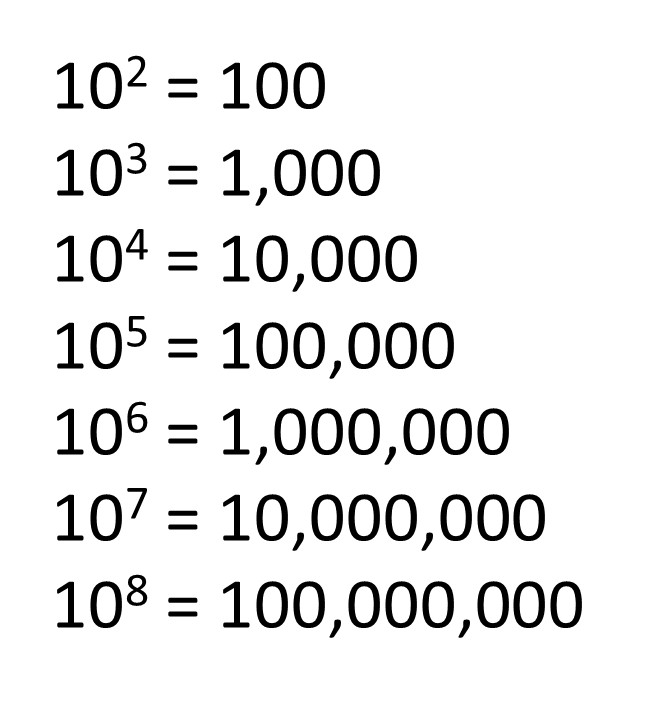In mathematics, a power of 10 is any of the integer powers of the number ten; in other words, ten multiplied by itself a certain number of times (when the power is a positive integer). By definition, the number one is a power (the zeroth power) of ten. The first few non-negative powers of ten are:
- 1, 10, 100, 1,000, 10,000, 100,000, 1,000,000, 10,000,000... (sequence A011557 in the OEIS)
Positive powers
In decimal notation the nth power of ten is written as '1' followed by n zeroes. It can also be written as 10n or as 1En in E notation. See order of magnitude and orders of magnitude (numbers) for named powers of ten. There are two conventions for naming positive powers of ten, beginning with 109, called the long and short scales. Where a power of ten has different names in the two conventions, the long scale name is shown in parentheses.
The positive 10 power related to a short scale name can be determined based on its Latin name-prefix using the following formula: 10[(prefix-number 1) × 3]
Examples:
- billion = 10[(2 1) × 3] = 109
- octillion = 10[(8 1) × 3] = 1027
For further examples, see Names of large numbers. Numbers larger than about a trillion are rarely referred to by name or written out as digits, but instead are typically described with exponent notation.
Negative powers
The sequence of powers of ten can also be extended to negative powers.
Similar to the positive powers, the negative power of 10 related to a short scale name can be determined based on its Latin name-prefix using the following formula: 10−[(prefix-number 1) × 3]
Examples:
- billionth = 10−[(2 1) × 3] = 10−9
- quintillionth = 10−[(5 1) × 3] = 10−18
Googol and googolplex
The number googol is 10100. The term was coined by 9-year-old Milton Sirotta, nephew of American mathematician Edward Kasner. It was popularized in Kasner's 1940 book Mathematics and the Imagination, where it was used to compare and illustrate very large numbers. Googolplex, a much larger power of ten (10 to the googol power, or 1010100), was also introduced in that book.
Scientific notation
Scientific notation is a way of writing numbers of very large and very small sizes compactly.
A number written in scientific notation has a significand (sometime called a mantissa) multiplied by a power of ten.
Sometimes written in the form:
- m × 10n
Or more compactly as:
- 10n
This is generally used to denote powers of 10. Where n is positive, this indicates the number of zeros after the number, and where the n is negative, this indicates the number of decimal places before the number.
As an example:
- 105 = 100,000
- 10−5 = 0.00001
The notation of mEn, known as E notation, is used in computer programming, spreadsheets and databases, but is not used in scientific papers.
See also
- Power of two
- Power of three
- SI prefix
- Cosmic View, inspiration for the film Powers of Ten
- Exponentiation
- Philip and Phylis Morrison wrote a book called "Powers of Ten: A Book About the Relative Size of Things in the Universe and the Effect of Adding Another Zero" to accompany the video of Eames. [1]
Further reading
- Video
- Powers of Ten (1977). Nine-minute film. US Public Broadcasting Service (PBS), made by Charles and Ray Eames. "An adventure in magnitudes. Starting at a picnic by the lakeside in Chicago, this film transports the viewer to the outer edges of the universe. Every ten seconds we view the starting point from ten times farther out until our own galaxy is visible only as a speck of light among many others. Returning to Earth with breathtaking speed, we move inward - into the hand of the sleeping picnicker - with ten times more magnification every two seconds. Our journey ends inside a proton of a carbon atom within a DNA molecule in a white blood cell."
References